At HostUp, we believe you should have complete control over your server—even when things go wrong. That’s why we’ve introduced Remote Commands in our customer portal. It’s a powerful tool that lets you run commands directly on your server through the QEMU Guest Agent—no SSH login required.
What can I use this for?
The tool is perfect for troubleshooting and rescue operations. Because the commands run directly through the hypervisor (the virtualization layer), you’re not dependent on the network—or on SSH running properly on the server. For example, you can:
- Restore SSH configurations that have gone wrong.
- Stop a firewall (UFW/IPTables) that is blocking your access.
- Check disk space or memory usage if the server feels sluggish.
- Change the default shell if login has stopped working.
How to Use Remote Commands
- Start by logging in to your customer zone at Log in to cloud.hostup.se if you are not already logged in and select the VPS you want to access:
- Click the Settings tab and select Remote Commands from the menu.
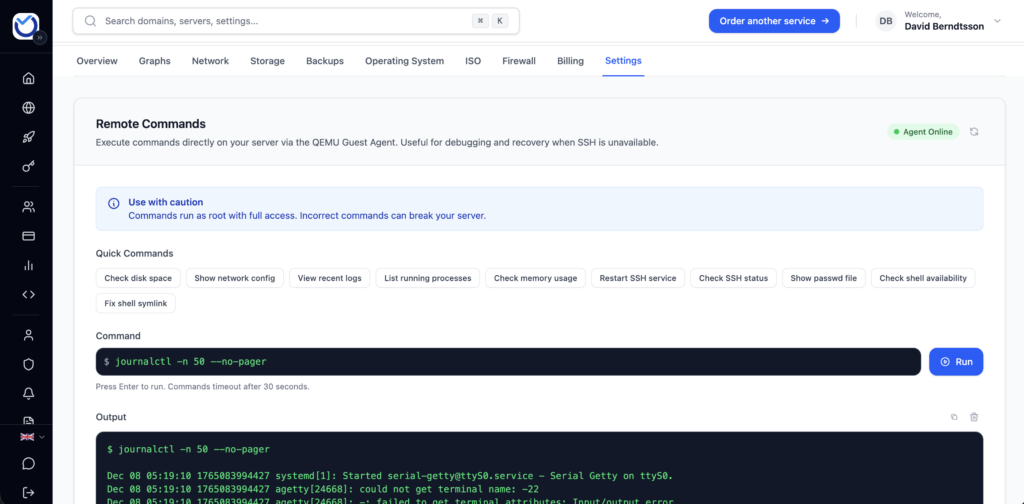
- Make sure the status in the top right shows Agent Online (green dot).
- Type your command in the box, or click one of our “Quick Commands,” and press Run.
Warning: Every command here runs as root with full privileges. Be careful what you type!
Real-world example: “Access Denied” after switching shells
A common mistake (one we’ve seen even the best make!) is changing your root shell to zsh or fish without actually installing it first.
The result? When you try to SSH in, you get an “Access Denied” error—or the session closes right away—because the server can’t find the program it’s supposed to start at login. You can easily see the error in the logs (journalctl -f), but if you can’t get into the server it becomes very hard to figure out what’s wrong—especially after you’ve already reset the password and still can’t access it.
Solution: Remote Commands
Previously, you had to pull up the console and hope you could log in, or boot into a “Rescue Image” to fix the issue. Now you can handle it yourself in just 30 seconds:
- Go to Remote Commands under Settings.
- Click the quick command Fix shell symlink (or enter it manually:
chsh -s /bin/bash root). - Press Run.
- All set! You can log in via SSH again.
Common commands you might need
Here are some handy commands to have on hand when your server is acting up:
- Check if the disk is full:
df -h - Restart the SSH service:
systemctl restart ssh - See the latest logs:
journalctl -n 50 --no-pager - Check who’s eating memory:
ps aux --sort=-%mem | head - Disable the firewall:
ufw disableoriptables -F
Still having trouble even after using Remote Commands? Of course, we’re here for you. Open a support ticket and we’ll help you out!
 English
English
 Swedish
Swedish
